1617. Blowing up the roads
There is a direct bidirectional road
between every pair of distinct towns in the country. Peter wants to blow up
enough of these roads that there are at least two towns that are no longer
connected to each other by any direct or indirect paths.
You are given the cost of blowing up each
road. Find the minimal total cost required for Peter to achieve their goal.
Input. Consists of multiple test cases. The first line of
each test case contains the number n (n ≤ 50) of towns in a
country. Next n lines describe the roads: the j-th character of
the i-th line is a digit representing the cost of blowing up the road
from the i-th town to the j-th town.
Output. For each test case print in a separate line the
minimal total cost required for Peter to achieve their goal.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
4 0911 9011 1109 1190 6 030900 304120 040174 911021 027207 004170 4 0399 3033 9309 9390 |
4 8 9 |
SOLUTION
graph - maximum flow
Algorithm analysis
Consider a graph
where cities are vertices and
two way roads are undirected
edges. According to the problem statement, it is necessary to remove from the graph such a set
of edges, which total cost is minimum. This is the classic minimum cut problem. At the same time, it is known that minimum
cut equals to maximum flow.
For any cut, the vertex 0 will be separated from some other. Therefore, find the maximum flow between vertices 0 and i (0
< i < n = |V|) and print the smallest among them.
Example
Consider the
first test
case. The maximum flow between vertices 0 and 2 is 4. The paths along which
the flow of size 4 moves are:
·
0 – 1 – 2, flow = 1;
·
0 – 2, flow = 1;
·
0 – 3 – 2, flow = 1;
·
0 – 1 – 3 – 2, flow = 1;
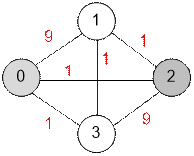
·
the maximum flow between nodes 0 and 1 is 11;
·
the maximum flow between nodes 0 and 3 is 4;
Algorithm realization
Declare the arrays. cap[i][j] contains the cost of destroying the road
between the i-th and j-th city.
#define MAX 50
int cap[MAX][MAX], res[MAX][MAX],
used[MAX];
The aug(x, t, CurFlow) function finds the residual capacity of the augmenting path
from x to t if the residual
capacity of the augmenting path from the start vertex to x equals to CurFlow.
int aug(int
x,int t,int
CurFlow)
{
if (x == t) return CurFlow;
if (used[x]++)
return 0;
for (int Flow, y = 0; y < n; y++)
{
if
(res[x][y] > 0 && (Flow = aug(y,t,min(CurFlow,res[x][y]))))
{
res[x][y] -= Flow; res[y][x] += Flow;
return
Flow;
}
}
return 0;
}
The function mincut(s, t) finds the maximum
flow between vertices s and t.
int mincut(int
s, int t)
{
memcpy(res, cap, sizeof(cap));
int x, flow =
0;
do
{
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
} while ((x =
aug(s,t,0x7FFFFFFF)) && (flow += x));
return flow;
}
Find the maximum flow from the vertex 0 to the vertex s (1 ≤ s
≤ n – 1). Among the found maximum flows, find the minimum.
int requiredCost(void)
{
int best =
0x7FFFFFFF;
for (int s = 1; s < n; s++)
best = min(best,mincut(0, s));
return best;
}
The main part of the program. Read the data for each test case and call the function requiredCost.
while(scanf("%d\n",&n)
== 1)
{
for (i = 0; i
< n; i++)
{
gets(s);
for (j = 0;
j < n; j++)
cap[i][j] = s[j] - '0';
}
printf("%d\n",requiredCost());
}
Algorithm realization – bfs, Edmonds - Karp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAX 50
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace std;
int cap[MAX][MAX], m[MAX][MAX],
used[MAX], parent[MAX];
int i, j, n;
string s;
void bfs(int v, int final)
{
queue<int>
q;
q.push(v);
used[v] = 1;
while
(!q.empty())
{
int from
= q.front(); q.pop();
if
(from == final) return;
for (int to =
1; to <= n; to++)
if
((m[from][to] > 0) && (!used[to]))
{
used[to] = 1;
parent[to] = from;
q.push(to);
}
}
}
void Rebuild(int k, int flow)
{
if
(parent[k] == -1) return;
Rebuild(parent[k], flow);
m[parent[k]][k] -= flow;
m[k][parent[k]] +=
flow;
}
int FindFlow(int k)
{
if
(parent[k] == -1) return INF;
int x =
FindFlow(parent[k]);
return
min(x, m[parent[k]][k]);
}
int Flow(int source, int final)
{
memcpy(m,
cap, sizeof(cap));
int
MaxFlow = 0;
while (1)
{
memset(parent,
-1, sizeof(parent));
memset(used,
0, sizeof(used));
bfs(source, final);
int flow
= FindFlow(final);
if
(flow == INF) break;
MaxFlow
+= flow;
Rebuild(final,
flow);
}
return
MaxFlow;
}
int requiredCost(int n)
{
int res
= INF;
for (int s =
1; s < n; s++) // vertices 0..n-1
res =
min(res, Flow(0, s));
return res;
}
int main(void)
{
while (cin
>> n)
{
memset(cap,
0, sizeof(cap));
for (i =
0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> s;
for (j =
0; j < n; j++)
cap[i][j] = s[j] - '0';
}
printf("%d\n",
requiredCost(n));
}
return 0;
}